SODIUM n-BUTOXIDE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
2372-45-4
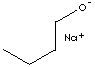
C4H9ONa
96.11
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Alkoxide (also called alcoholate ) is the conjugate bases of corresponding alcohol. They contain negatively charged oxygen atom, found as intermediaries in various reactions. Alkoxide is a strong reducing agent. The term alkoxide is for a compound formed from alcohol by replacing the hydrogen of the hydroxy group by a monovalent metal. Metal alkoxides are versatile reagents favoring the chemical reaction of condensation, esterification, alkoxylation and etherification, Claisen condensation, Wolf-Kishner reduction and Stobbe reaction are examples. They are used in wide range of applications in organic synthesis; Agrochemicals; Pharmaceuticals, colorants and aroma chemicals. They are used in manufacturing detergents and biodiesel. They also act as catalysts in polymerization and isomerizations.
- Alkylation
Inorganic superbases are typically salts with highly charged, small negative ions, e.g. lithium nitride, which has extreme negative charge density and so is highly attracted to acids, like the aqueous hydronium ion. Alkali and earth alkali metal hydrides (sodium hydride, calcium hydride) are superbases.
The base strength can be varied with choice of solvent and the structure of the alcohol. In the dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), the ion aggregates are solvated thus increasing the basicity. Alkyl groups in steric bulk of the tertiary alcohol make the alcoholate a stronger base compared to primary alcoholates and hydroxides and influence the speed, selectivity, and specificity. Generally primary alcoholate is soluble in the alcohol from which they are derived only. But sec-, and tert- alcoholates are soluble in ethers. Furthermore tert- alcoholates have high solubility in the hydrocarbons. In organic synthesis, higher solubility of tertiary alcoholates can generate " Schlosser base (or Lochmann-Schlosser base)" in combination with an alkyl lithium to. The Schlosser base is a commonly used superbase. Butyllithium exists as four-, or six-membered clusters, which are kinetically slow to react. The tertiary alcoholate (butoxide) serves to complex the lithium ion, which breaks the butyllithium clusters. This makes the butyllithium kinetically more reactive. Other such systems are collectively called harpoon bases.
|
Alcoholate |
CAS RN |
| Sodium Methylate | 124-41-4 |
| Sodium Ethylate | 141-52-6 |
| Sodium n-Propylate | 6819-41-6 |
| Sodium Isopropylate | 683-60-3 |
| Sodium n-Butylate | 2372-45-4 |
| Sodium tert-Butylate | 865-48-5 |
| Sodium tert-Amylate | 14593-46-5 |
| Sodium n-Hexylate | 19779-06-7 |
| Sodium mentholate | 19321-38-1 |
| Potassium Methylate | 865-33-8 |
| Potassium Propylate | 16872-93-8 |
| Potassium Isopropylate | 6831-82-9 |
| Potassium Butylate | 589-39-9 |
| Potassium n-Butylate | 3999-70-0 |
| Potassium tert-Butylate | 865-47-4 |
| Potassium tert-Amylate | 41233-93-6 |
| Potassium-3,7-Dimethyl-3-Octylate | 263148-42-1 |
APPEARANCE
20%